
Introduction: The Global Expansion of GCCs
Global Capability Centers (GCCs) have evolved from cost-reduction hubs to strategic assets driving innovation and operational excellence across multinational enterprises. These centers now deliver high-value services spanning IT, analytics, R&D, customer experience, and specialized knowledge work, requiring sophisticated GCC location strategy that balances talent availability, operational costs, and market dynamics.
While India maintains its position as the established GCC powerhouse with unmatched scale and depth, the landscape is rapidly diversifying. Southeast Asian markets, particularly the Philippines, are emerging as compelling alternatives that offer complementary advantages for specific operational models and strategic objectives in the broader APAC GCC market comparison.
This is where platforms like Altre help global occupiers compare top APAC markets, combining real-time competition and talent insights, regulatory intelligence, and real estate & talent analytics to make smarter location decisions. This data-driven approach becomes increasingly crucial as companies navigate a complex matrix of location factors when establishing global capability centers.
The Philippines positions itself as a strategic complement to traditional GCC destinations. Driven by exceptional English proficiency, cultural alignment with Western markets, competitive cost structures, and operational agility, the Philippines offers multinational companies a unique value proposition for establishing or expanding their global capability footprint in an increasingly sophisticated and competitive landscape.
Why is the Philippines Emerging as the New GCC Hub?
The Philippines is experiencing unprecedented growth in its GCC market, with projections showing the market will reach USD 67.97 billion by 2032, representing a doubling from USD 32.5 billion in 2023. This remarkable expansion reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.04%, significantly outpacing many other emerging markets and positioning it as a serious alternative in India vs Philippines GCC discussions.
Language Competency and Cultural Alignment
The Philippines leads globally in language competency, ranking 14th worldwide with a remarkable 92.5% proficiency rate in English and neutral accent. This exceptional linguistic capability, combined with Filipinos'cultural alignment with Western business practices, makes them particularly well-suited for customer-facing roles and complex knowledge work - areas where Philippines vs India outsourcing comparisons often favor the Philippines.
Strong Talent Pipeline
The country produces over 700,000 annual graduates, with a strong emphasis on STEM and business fields. This large, educated, and highly adaptable talent pool provides companies with access to skilled professionals who can seamlessly integrate into global operations and understand international business standards. When comparing the cost of talent India vs Philippines, the Philippines offers highly cost-efficient operations while maintaining quality standards, with average software engineer salaries approximately INR 6 LPA and monthly living costs averaging INR 60K/month.
Strategic Geographic Positioning
The country's geographic location enables optimal time zone overlap with Asia-Pacific, Australia, and North America, particularly aligned with US time zones, facilitating effective "follow-the-sun" service models that ensure continuous 24/7 business operations across global markets.
Government Support and Policy Framework
The Philippine government has implemented comprehensive policies to support GCC growth, with agencies like the Philippine Economic Zone Authority (PEZA) and Board of Investments (BOI) providing streamlined processes and attractive incentives for establishing operations.
Key Business Hubs and Cities
The Philippines offers multiple strategic locations for GCC operations across major urban centers:
Primary Business Hubs:
-
Metro Manila - The capital region and primary business center, housing the majority of multinational corporations and financial institutions
-
Metro Cebu - The second-largest urban center, emerging as a major IT-BPO hub with modern infrastructure
-
Davao Region - Strategic location in Mindanao with a growing IT services sector and government support
-
Taguig City - Part of Metro Manila, home to Bonifacio Global City (BGC), a premier business district
-
Quezon City - The largest city by population in Metro Manila with established commercial districts
-
Calabarzon - Economic region covering Cavite, Laguna, Batangas, Rizal, and Quezon provinces, offering proximity to Manila with lower operational costs
These locations feature modern office parks and mixed-use developments specifically designed to cater to GCCs and IT-BPM firms, offering world-class facilities with advanced telecommunications infrastructure, reliable power systems, and modern amenities.
Sector and Company Distribution
The Philippines'GCC ecosystem spans multiple high-value sectors, with Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) leading with a 31% market share. The country has developed niche strengths in customer experience (CX), BPO, and finance operations.
IT and IT-enabled Services (ITES) and Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO) remain dominant sectors, though the landscape differs notably from India's technology-heavy focus. While India has established itself as a global IT services powerhouse with deep technical capabilities in software development and complex system integration, the Philippines has carved out a complementary position emphasizing application support, maintenance, and user-facing services.
Manufacturing and automotive industries are experiencing rapid growth, and healthcare services are emerging as a significant growth area in the Philippines. R&D, analytics, and digital transformation services are expanding rapidly beyond traditional BPO functions, representing the Philippines'evolution toward higher-value IT work similar to India's trajectory in AI and R&D hubs.
IT Sector Positioning Comparison
The IT sector comparison reveals distinct positioning in India vs Philippines IT services:
-
India dominates in custom software development, enterprise solutions, and technical consulting
-
Philippines excels in IT support services, application management, and technology-enabled business processes
This creates opportunities for companies to leverage both markets strategically through a dual-shore strategy India and Philippines approach, utilizing India for complex development work and the Philippines for operational support and customer-facing technology services.
Major Industry Players:
Leading companies that have established or expanded their Philippine GCC operations include Accenture, IBM, Concentrix, Toyota Motor Philippines, Deloitte, Thomson Reuters, Teleperformance, and Sitel Group.
Talent, Skills, and Labor Market
The Philippines'IT sector benefits from over 700,000 annual graduates, with a robust STEM pipeline specifically supporting technology roles. Filipino IT professionals demonstrate high emotional intelligence and global fluency, making them particularly effective in customer-facing technology roles and IT service delivery.
The adaptability and cultural alignment of Filipino IT workers facilitate seamless integration for multinational technology companies, often requiring less cultural bridging compared to other offshore locations.
Workforce Distribution
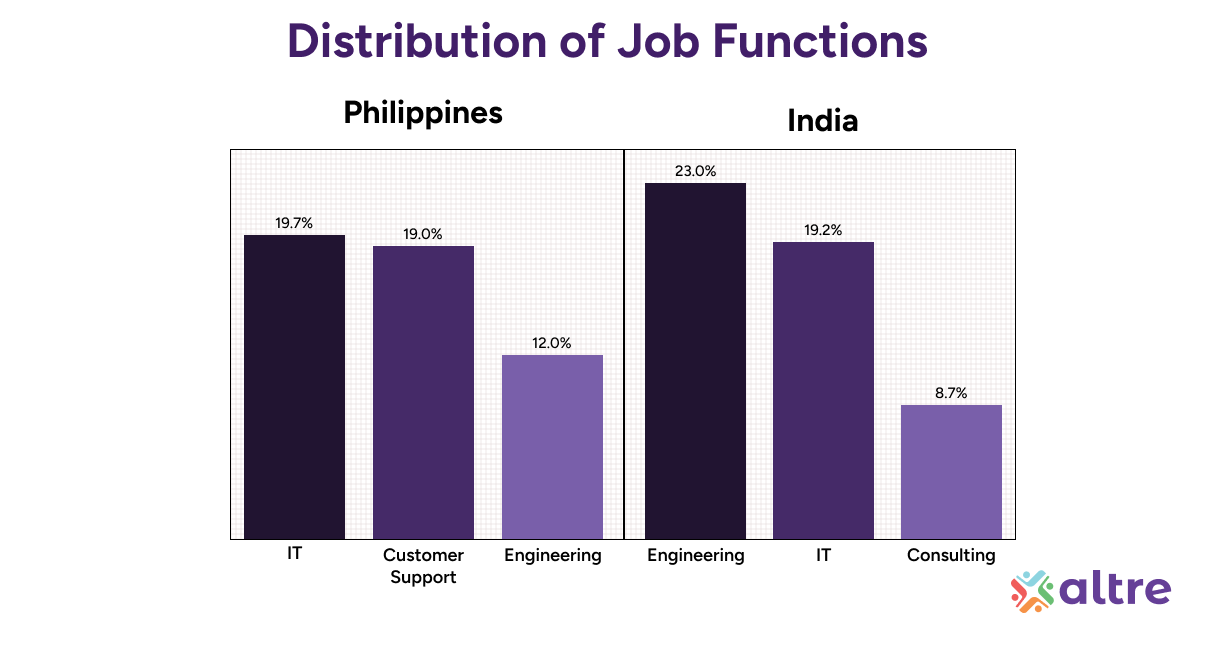
Within the Philippines'IT sector workforce distribution:
-
19.7% employed in core IT functions
-
19% in Customer Success and Support (often technology-enabled)
-
12% in Engineering tasks
This distribution reflects the Philippines'positioning in IT operations, support, and maintenance. GCC employment in IT is expanding beyond Metro Manila to provincial cities like Cebu, Davao, and Iloilo, diversifying talent access while maintaining cost advantages.
Real Estate Infrastructure Development
The Philippine real estate market has reached USD 90.51 billion in 2024, driven by urbanization, economic growth, and increasing demand for both commercial and residential spaces in key urban centers. The market offers competitive rental rates for IT operations ranging from Rs.55.3/sqft/month in Bacolod to Rs.140.61/sqft/month in Metro Manila, significantly lower than office space costs in India's major GCC hubs.
Purpose-built business districts and enhanced telecommunications infrastructure support growing IT sector demand. Government infrastructure initiatives and overseas Filipino worker (OFW) remittances continue to fuel property development and investment, creating a robust foundation for continued GCC expansion.
Key developments include:
-
Improved transportation networks
-
Enhanced telecommunications infrastructure
-
Modernized business districts specifically designed for international operations
-
Flexible workspace solutions catering to evolving GCC needs
Employee Benefits and Regulatory Framework
The Philippines offers a comprehensive and attractive employee benefits structure that supports both employer and employee interests:
Mandatory Social Security Contributions
Social Security System (SSS) - State-run program providing social insurance to Filipino workers
-
Covers sickness pay, maternity benefits, disability benefits, pension, and life insurance
-
Total contribution: 11% of monthly salary (employer: 7.37%, employee: 3.63%)
-
Maximum contribution base: PHP 16,000
PhilHealth (Universal Health Insurance) - Covers hospitalization expenses for all employees
-
Contribution rate: 5% of monthly basic salary (employer and employee split equally)
-
Enhanced coverage under the Universal Health Care Law (Republic Act 11223)
Leave Benefits
Service Incentive Leave (SIL)
-
Minimum 5 days paid leave annually for all employees
Maternity Leave
-
105 days of paid maternity leave for female employees with an option to extend 30 additional unpaid days
Paternity Leave
-
7 days paid leave for married male employees, applicable for up to 4 deliveries of a legitimate spouse
Specialized Leave Types
-
Single Parent Leave: 7 working days annually with full pay
Additional Benefits
13th Month Pay
-
Mandatory additional month's salary (1/12 of annual salary)
-
Tax-exempt benefit payable by December 24
Working Hours and Overtime
-
Standard workweek: 40 hours (8 hours daily)
-
Overtime compensation: 1.25x regular hourly wage
-
Sunday/holiday work: 1.3x regular hourly rate
-
Night shift differential: Minimum 10% of regular hourly wage (10 PM - 6 AM)
-
Holiday pay: 200-260% of the regular rate
Retirement Benefits
-
Employees reaching age 60-65 receive ½ monthly salary per year of service
-
Minimum of 5 years of service required to avail the benefit
Challenges and Opportunities
Current Challenges
Scale Development: The Philippines currently hosts approximately 150 GCCs compared to India's establishment of 100+ new GCCs annually, highlighting the scale gap in GCC growth India vs Philippines.
Infrastructure: While improving, certain infrastructure elements require continued development to support large-scale GCC expansion in secondary cities.
Natural Disaster Risk: High level of disaster risk due to geographic location, making it vulnerable to various natural hazards.
Regional Competition: Increasing competition from other emerging markets in Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe.
Significant Opportunities
Higher Revenue Productivity: GCCs in the Philippines typically generate higher revenue per employee compared to traditional outsourcing models.
Provincial Expansion: Significant opportunities exist for expanding GCC operations into provincial cities with access to untapped talent pools and competitive cost structures.
Digital Transformation Leadership: Well-positioned to serve as a regional innovation hub for digital transformation initiatives.
Specialized Service Development: Growing opportunities in healthcare analytics, financial technology, and advanced manufacturing support services.
Sustainability Focus: Increasing emphasis on green and sustainable office solutions aligns with global ESG requirements.
Philippines vs India: Strategic Positioning
The Philippines and India offer complementary rather than competing value propositions in the global GCC landscape. While India maintains its dominance with over 1,580 established GCCs and unmatched scale in complex technical services, the Philippines emerges as the preferred destination for customer-facing operations, application support, and agile service delivery.
Comparative Strengths:
India's Strengths:
-
Deep technical expertise and large-scale engineering capabilities
-
Mature ecosystem with proven track record
Philippines'Strengths:
-
Cultural alignment and communication excellence
-
Operational flexibility and faster decision-making
-
Higher service orientation
-
Cost-effective talent with strong English proficiency
This positioning creates opportunities for multinational companies to adopt a dual-shore strategy, leveraging India's technical depth for complex development work while utilizing the Philippines'cultural and linguistic advantages for customer engagement and operational support. The Philippines'faster decision-making processes and higher service orientation complement India's established infrastructure and technical maturity, offering companies a comprehensive approach to global capability distribution.
The Future of APAC GCC Markets
As the global capability center landscape continues to evolve, the best country for GCC setup depends increasingly on specific business requirements, risk tolerance, and strategic objectives. The Philippines represents a compelling option for companies seeking:
-
Strong customer-facing capabilities
-
Cultural alignment with Western markets
-
Cost-effective operations with quality delivery
-
Agile and flexible service models
-
English-language proficiency at scale
Meanwhile, India's outsourcing advantage remains strong for companies requiring deep technical expertise, large-scale operations, and complex engineering capabilities.
Conclusion: The Philippines'GCC Future
While the Philippines has positioned itself as a rising star in the global GCC landscape with impressive 12.04% CAGR and projected growth to USD 67.97 billion by 2032, it's important to recognize that India remains the undisputed global leader in GCC operations. With over 1,580 established GCCs, unmatched technical expertise, and a proven track record spanning decades, India's outsourcing advantage continues to drive the majority of global capability center investments.
The Philippines'success stems from its unique value proposition as a complementary destination: superior English proficiency, cultural compatibility with Western markets, and exceptional service quality in customer-facing operations. However, these strengths position the Philippines not as a replacement for India, but as an ideal partner in sophisticated dual-shore strategies that leverage India's technical depth for complex engineering and development work.
India's established ecosystem offers irreplaceable advantages: mature infrastructure in Bangalore, Hyderabad, Pune, and emerging tier-2 cities; deep talent pools in AI, R&D, and advanced technology; and established partnerships with global enterprises across BFSI, healthcare, and manufacturing sectors.
As multinational companies increasingly adopt sophisticated location strategies, the optimal approach combines India's technical excellence and scale with the Philippines'service-oriented strengths. India remains the anchor for complex, high-value operations, while the Philippines serves as an effective complement for customer experience, operational support, and specific regional requirements.
The future of global capability centers lies not in choosing between these markets, but in strategically leveraging both. India's continued dominance in core GCC functions, combined with selective use of complementary markets like the Philippines, offers enterprises the most comprehensive approach to global operations optimization. This dual-shore model ensures companies can access India's unmatched technical capabilities while utilizing the Philippines'cultural and linguistic advantages where most effective.


